Monarch Blog
We're on a mission to make better financial outcomes available to everyone. Read our latest thoughts and insights.
Featured
Flex Budgeting: Simplify Your Spending With Just One Number
Monarch's Head of Advice Rachel Lawrence on the simple budgeting method that works for the vast majority of people who try it.
Categories
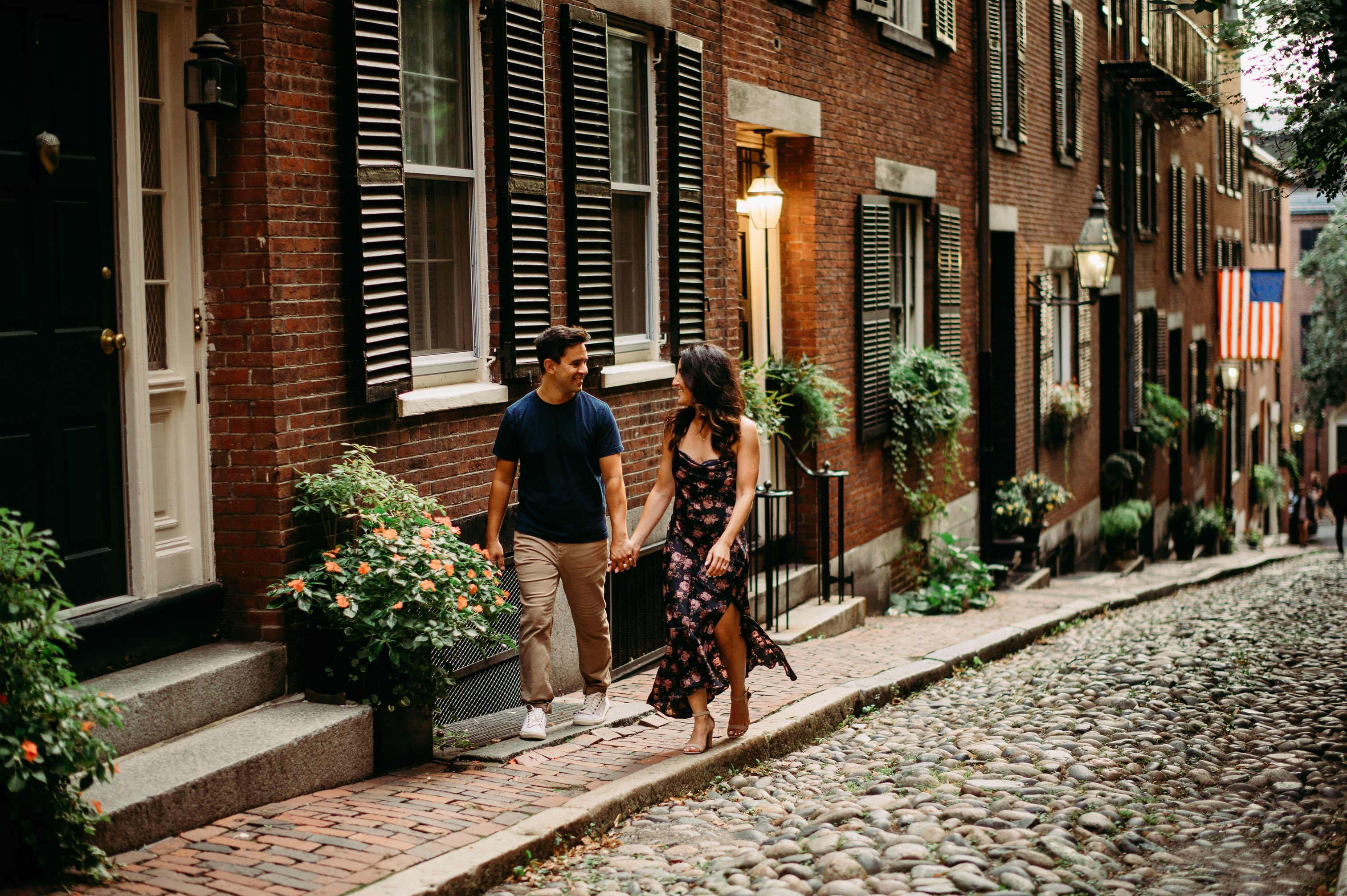

December 10, 2024
Saving For Our Dream House Sounded Stressful. Then We Found Monarch.
The story of Trent and Lauren, who crushed their savings goals and minimized arguments after they started using Monarch.

December 3, 2024
A Beginner's Guide to Mortgage Loans
For the average American buying a home, a mortgage loan is an absolute necessity. But just because it’s common, doesn’t mean the decision to be taken lightly. Discover what a mortgage loan is and how it works before you start your house hunt.
November 18, 2024
Money Diaries: The Inside Scoop of a Child-Free, 30-Something Couple’s Finances
We’re pulling back the veil to show you real finances from a real 30-something couple, so you can identify opportunities to improve your own finances, preventing stress and protecting your relationship along the way.

November 17, 2024
Flex Budgeting: Simplify Your Spending With Just One Number
Monarch's Head of Advice Rachel Lawrence on the simple budgeting method that works for the vast majority of people who try it.

November 16, 2024
Should You Pay Off Your Mortgage Early? Pros, Cons, & Considerations
You have some extra cash. Congratulations! Here's how to figure out whether paying off your house makes sense for you and your family.

November 15, 2024
Flex vs. Category Budgeting: How to Choose What's Right for You
Monarch’s Head of Advice Rachel Lawrence on how to choose the budgeting method that works for your finances and your lifestyle.

November 10, 2024
We Used to Argue About Money. Then We Got Monarch.
“Now my money anxiety has gone from 100% to less than 10%. It’s been night and day.”

October 30, 2024
How to Understand — and Overcome — Difficult Emotions Around Money
Money may seem logical, but it’s actually quite emotional for most people. Here’s how to keep that from holding your finances back.

October 15, 2024
Renting Versus Buying: Pros, Cons, & Considerations
It was once true that most people defaulted to buying a home, but times have changed. Here’s how you can get some clarity on whether to buy or not.
Subscribe to our personal finance newsletter
Sign up with your email to receive all our latest blog posts directly in your inbox.


September 18, 2024
What is Probate, and Why Should You Care?
When you avoid estate planning, the state will handle your estate — whether it aligns with your wishes or not.
September 13, 2024
Are Credit Card Points Worth It? Mostly.
How to figure out if your rewards credit card is costing you.
August 30, 2024
Pre-built iOS Binaries: Reducing React Native Dev Start Time from Minutes to Seconds
Using pre-built binaries, we reduced our React Native app build time from minutes to seconds.